| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
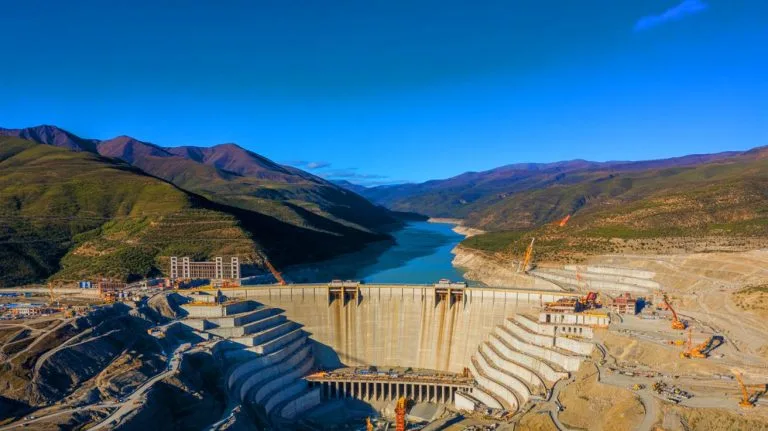
The ambitious Moyuo project, a colossal hydroelectric endeavor, is set to redefine the limits of engineering and geopolitics. Situated on the Tibetan plateau, it promises to generate an immense 60 gigawatts of electricity, surpassing the already monumental Three Gorges Dam. While the potential energy benefits are substantial, the project’s location and scale have sparked both interest and controversy. As China seeks to secure its energy future, it also faces scrutiny over environmental and geopolitical implications. This balancing act of progress and precaution raises questions about the future of energy, water security, and regional diplomacy in Asia.
Unprecedented Scale in the Heart of Tibet
The Motuo dam, valued at a staggering $165 billion, represents China’s relentless pursuit of energy dominance. With a planned capacity of 60 gigawatts, it aims to eclipse the Three Gorges Dam’s 22 gigawatts, positioning itself as a leader in renewable energy. The strategic placement on the Tibetan plateau, at the headwaters of the Yarlung Tsangpo river, underscores China’s focus on harnessing natural resources efficiently. This location is not just advantageous for energy production; it also plays a crucial role in managing water resources in a region where water scarcity is a growing concern.
China’s energy policy is characterized by an aggressive expansion of both renewable and thermal energy sources. The country leads globally in solar panel installations and continues to build coal-fired power stations. Within this framework, hydroelectric power offers a controllable, carbon-free energy source. The Motuo dam is a pivotal element in this strategy, representing one of 193 hydroelectric projects, 80% of which boast capacities exceeding 100 megawatts.
The implications of the Motuo project extend beyond energy production. By controlling the headwaters of major river basins, China wields significant influence over water resources that are vital to its population. As the nation contends with limited freshwater reserves, strategic projects like Motuo are crucial to securing long-term water and energy sustainability.
Water Control and Geopolitical Tensions
The construction of the Motuo dam is emblematic of China’s broader strategy to manage its water resources while extending its geopolitical influence. This approach, however, is not without controversy. The International Campaign for Tibet (ICT) has raised concerns about the lack of local consultation, highlighting the potential displacement of up to a million people if ongoing projects proceed. This displacement issue is a significant structural challenge, with 120,000 individuals already affected by similar developments in the region.
Geopolitically, the Motuo dam has the potential to disrupt regional stability. Its location on the Yarlung Tsangpo river, which flows into India and eventually Bangladesh, has prompted diplomatic tensions. Despite Beijing’s assurances that the dam will not negatively impact downstream regions, India has voiced its determination to protect its water interests. In a region where 1.8 billion people depend on these vital water resources, any disruption could have far-reaching consequences.
Additionally, the feasibility of the Motuo project is under scrutiny due to the Tibetan plateau’s seismic activity. Constructing such a massive structure in a seismically active zone raises questions about its long-term stability. Furthermore, climate change exacerbates these concerns, as melting glaciers and unpredictable weather patterns alter river flows, posing risks to both the dam’s profitability and safety.
Environmental and Economic Implications
The environmental ramifications of the Motuo dam are profound. Large-scale hydroelectric projects often significantly impact ecosystems, affecting biodiversity and altering riverine environments. The potential for habitat disruption and changes in fish populations is a pressing concern for environmentalists. Moreover, the construction and operation of such a massive structure could exacerbate existing environmental challenges in the region.
Economically, while the dam promises significant returns through energy production, the costs associated with potential environmental damage and displacement of communities could offset these gains. Balancing economic benefits with environmental preservation and social equity is a complex challenge that requires careful planning and execution.
As China continues to pursue ambitious projects like the Motuo dam, it must navigate the intricate web of environmental, economic, and social responsibilities. Ensuring that these endeavors contribute positively to both local communities and the global environment is crucial for sustainable development.
The Future of Hydroelectric Power in China
The Motuo dam exemplifies China’s commitment to expanding its hydroelectric capacity as part of a broader energy strategy. However, the challenges it faces are indicative of the complexities involved in large-scale infrastructure projects. As the nation seeks to reduce its carbon footprint and transition to renewable energy, hydroelectric power remains a key component of this strategy.
Yet, the sustainability of such projects hinges on addressing the myriad challenges they present. From geopolitical tensions to environmental concerns, the path forward requires innovative solutions and international collaboration. As China continues to lead in renewable energy development, it must also consider the broader implications of its projects on regional stability and global environmental health.
In an era where energy security and environmental sustainability are paramount, how will China balance its ambitious energy goals with the need for responsible stewardship of natural resources and regional diplomacy?
Did you like it? 4.2/5 (24)







Wow, $165 billion! I wonder how many Starbucks frappuccinos that could buy? 🤔
Is this dam project really worth the $165 billion price tag? 🤔