| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
In the ever-evolving landscape of construction materials, a groundbreaking innovation has emerged that could redefine how we think about infrastructure. Researchers have developed a remarkable cement-hydrogel composite that not only provides structural integrity but also generates and stores electricity. This revolutionary material, inspired by the natural architecture of plant stems, is poised to play a pivotal role in the development of smart cities, offering a more sustainable and efficient approach to urban growth.
Cement’s Hidden Potential Unveiled
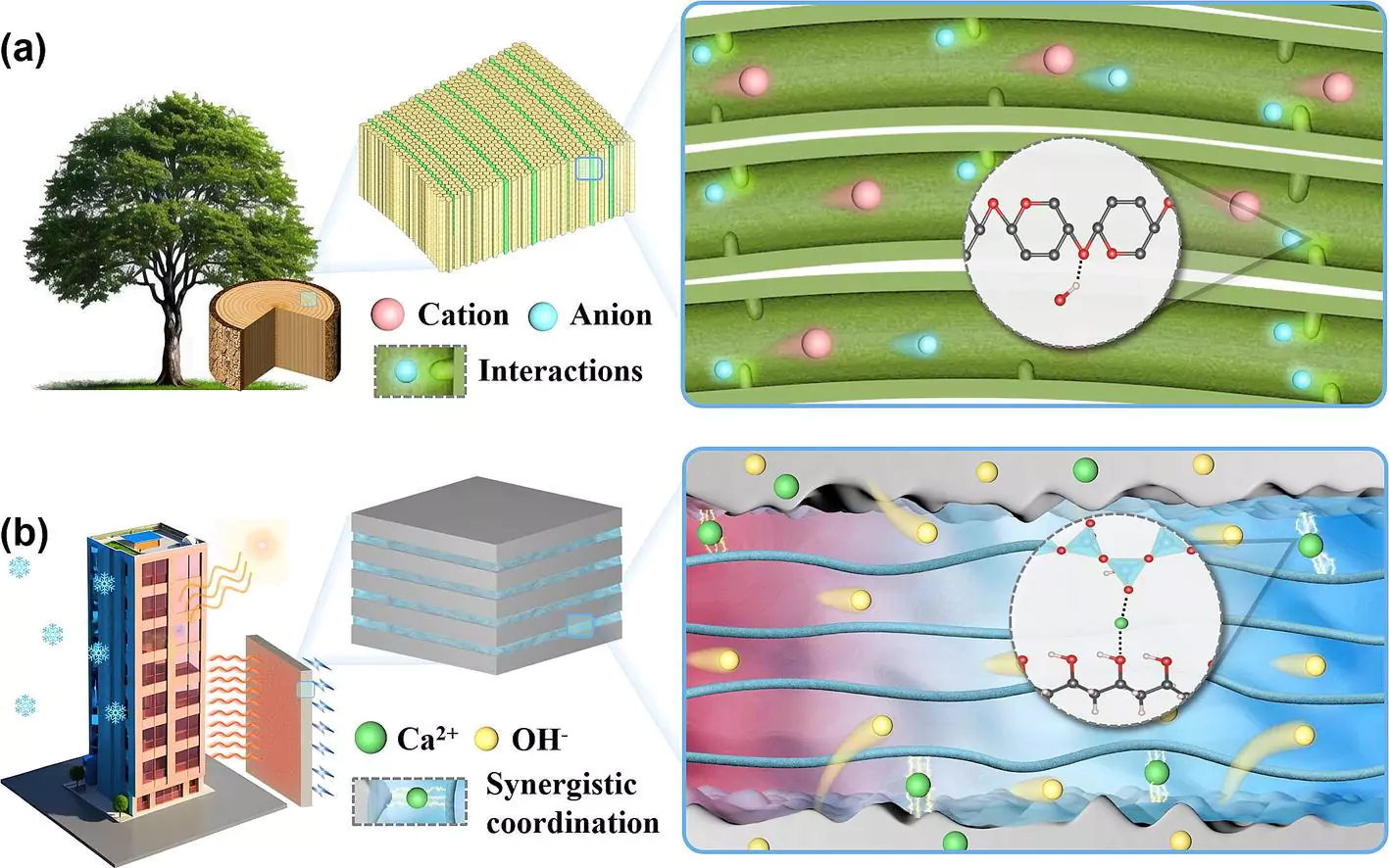
Cement has long been a staple in construction, known primarily for its structural capabilities. However, it possesses a lesser-known property called the ionic thermoelectric effect, which allows it to generate electricity. This effect, while fascinating, has been historically too weak to harness effectively. The dense matrix of cement restricts the movement of ions, thus limiting its ability to produce significant electrical output.
The team of researchers, led by Professor Zhou Yang at Southeast University in China, tackled this limitation by creating a multilayered structure that alternates between traditional cement and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel layers. This innovative design addresses the ion mobility problem, allowing for faster movement of hydroxide ions and enhancing the thermoelectric properties of the material. The result is a cement-hydrogel composite that significantly outperforms previous cement-based thermoelectric materials, boasting a Seebeck coefficient of −40.5 mV/K and a figure of merit (ZT) of 6.6×10⁻².
“UK’s robotic hound takes over” – This remote-controlled dog now conquers deadly nuclear zones
Smart Structures with Built-In Power
Beyond its ability to generate electricity, this new material also offers the remarkable capability of energy storage. The multilayered architecture not only strengthens its mechanical properties but also provides built-in energy storage capabilities. This means that infrastructure such as buildings, roads, and bridges could potentially power sensors and wireless communication systems embedded directly into the structures themselves.
The researchers emphasize that the biomimetic structure and interfacial selective immobilization mechanism of this composite pave the way for the development of high-performance ionic thermoelectric materials. Envision a future where sidewalks power streetlights or bridges monitor their own structural health, all without the need for external power sources. As cities continue to expand and smart technologies become more prevalent, materials like the cement-hydrogel composite offer a glimpse into a more efficient and sustainable urban environment.
Addressing Carbon Emissions in Construction
At the SynBioBeta: The Global Synthetic Biology Conference, industry experts will discuss ongoing challenges in reducing carbon emissions from the concrete industry. The session titled “Conquering Carbon Emissions From the Concrete Industry” will highlight how bioengineered materials, such as the newly developed cement composite, could play a critical role in advancing sustainable construction practices.
Concrete production is a major contributor to global carbon emissions, and the introduction of environmentally friendly alternatives like the cement-hydrogel composite could help mitigate this impact. By harnessing the unique properties of this innovative material, the construction industry can move towards more sustainable practices, reducing its environmental footprint while enhancing the functionality of infrastructure.
Pioneering the Future of Construction
The development of this cement-hydrogel material marks a significant milestone in the journey towards more sustainable construction solutions. By leveraging the inherent properties of cement and enhancing them through bio-inspired design, researchers have opened the door to a new era of infrastructure development. This material not only promises to improve the efficiency of energy generation and storage but also aligns with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable urban growth.
As cities around the world continue to evolve, the integration of smart technologies into infrastructure will become increasingly important. The cement-hydrogel composite offers a viable solution to meet these demands, providing a foundation for the cities of tomorrow. How will this innovation shape the future of urban development, and what other groundbreaking materials might emerge to further transform the construction industry?
Did you like it? 4.4/5 (24)








Wow, concrete that generates electricity? I never thought I’d see the day! ⚡️
How exactly does this new cement store energy? Is it like a battery?
Is it safe to walk on this electric cement? I don’t want a shocking experience! 😅
Thank you for sharing this incredible breakthrough! It’s exciting to see innovation in construction.
This sounds too good to be true. What’s the catch? 🤔
Can this cement be used in existing structures, or is it only for new builds?
Does generating electricity with this cement affect its durability or strength?
I’m curious about the cost. Is this new cement affordable for widespread use?
Finally, a way to reduce carbon emissions in construction! This is huge.
Will this cement be available worldwide, or just in certain regions?
I’m just imagining roads that charge electric cars as they drive. Future is here! 🚗⚡
What kind of maintenance does this type of cement require? Any special care?
How long can this cement generate electricity? Does its efficiency decrease over time?
Hope it doesn’t crack under pressure. Literally. 😂
Can this cement withstand extreme weather conditions like regular cement?
Imagine sidewalks that power streetlights. Such a brilliant idea. 🌟
I wonder how this innovation will affect the concrete industry’s job market.
Is there any risk of electric leakage? Safety first! ⚠️
What inspired researchers to mimic plant stems for this development?
Great article! This is a game-changer for sustainable construction. 🌿
Would this technology work on Mars? Asking for a friend. 😜
Any plans to integrate this cement technology with other renewable energy systems?
Could this be used in ocean structures? Curious about its potential underwater.
Awesome innovation, but how long before it’s commercially available?
It would be interesting to know the environmental impact of producing this cement.
I hope this doesn’t mean we’ll have to pay an electricity bill for our sidewalks! 😆
What’s the lifespan of this cement compared to traditional options?
How does the efficiency of this cement compare to solar panels?
Really cool! Does this mean buildings can become self-sustaining in the future?
Can this cement be recycled like regular cement after its lifecycle?
Sounds amazing, but how does it perform in terms of insulation?
Can this cement be colored or is it just the usual gray?
I’m impressed! This could revolutionize urban planning and architecture. 🏙️
Is the cement-hydrogel composite environmentally friendly to produce?
This was extremely amazing to read and I’ve learnt a lot from it !!!