| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
The story of the rose is one of beauty, evolution, and mystery. Researchers in China have made a groundbreaking discovery that traces the modern red rose back to a 30-million-year-old yellow ancestor. This finding sheds light on the evolutionary journey of one of the world’s most beloved flowers. An extensive genetic analysis conducted by French and Dutch scientists has unraveled this botanical mystery, offering new insights into rose breeding practices, especially in the face of climate change. As roses continue to captivate hearts worldwide, understanding their origins may revolutionize how we cultivate them in the future.
The Search for the First Rose
Throughout history, the rose has been a symbol of beauty and love, captivating people across continents. As researchers delved into its origins, they discovered that the rose’s history stretches back 30 million years. For years, scientists from Beijing Forestry University have been on a quest to uncover the ancient roots of this flower. They have conducted genetic analyses, field investigations, and fossil studies to piece together an evolutionary tree of the rose family.
Historical records suggested that roses were first cultivated in imperial gardens in China, as mentioned by Confucius. The recent study confirmed this, revealing that rose cultivation began around 5,000 years ago in China. The study also highlighted that many of today’s popular rose varieties are hybrids with Chinese species. During the late eighteenth century, the rose underwent significant changes as European and Chinese cultivars were engineered to enhance traits like fragrance and color.
The First Rose Was Yellow
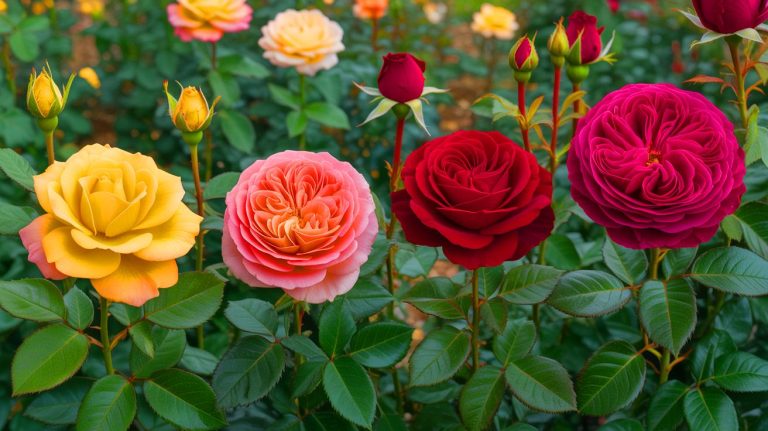
The discovery that the original rose was yellow and had single-petal flowers is both surprising and enlightening. The study revealed that the common ancestor of modern roses likely had seven leaflets and yellow blooms. Despite the vast diversity of over 35,000 rose cultivars today, all can be traced back to this single source. This revelation underscores the incredible evolutionary journey of roses over millions of years.
In the face of climate change, the significance of this finding cannot be overstated. Wild roses, with their inherent genetic diversity, are becoming increasingly important as cultivated varieties require genetic support to thrive. The research provides a solid foundation for future rose breeding efforts, emphasizing the need to use wild resources for innovative breeding practices. The rose’s journey from a yellow ancestor to the modern red rose is a testament to nature’s complexity and resilience.
Revolutionizing Rose Breeding Practices
The implications of this research extend beyond historical curiosity; it has the potential to revolutionize rose breeding practices. By understanding the genetic makeup of wild and cultivated roses, scientists can develop strategies to enhance the resilience and diversity of modern roses. This is particularly crucial as climate change poses new challenges for cultivating these beloved flowers.
The study highlights the importance of preserving wild rose species, which hold the key to unlocking genetic traits that can benefit cultivated varieties. As breeders look to the future, they must consider the genetic diversity found in wild roses to ensure the continued success of rose cultivation. This research paves the way for innovative approaches that could lead to more robust and adaptable roses, capable of thriving in changing environmental conditions.
The Ongoing Legacy of the Rose
The rose’s journey from a simple yellow flower to a global symbol of beauty and love is a testament to its enduring appeal. As scientists continue to explore its origins, they open new doors to understanding the intricate web of life on Earth. The findings from this study not only enrich our knowledge of roses but also prompt us to consider the broader implications for plant conservation and breeding efforts.
As we contemplate the future of rose cultivation, we must ask ourselves: how can we best preserve the genetic legacy of wild roses while ensuring the continued beauty and diversity of cultivated varieties? The answer to this question may hold the key to a flourishing future for one of the world’s most cherished flowers.
Did you like it? 4.6/5 (25)








Wow, I had no idea roses were originally yellow! 🌼